SmartVote
Create, manage and join voting sessions
Introduction
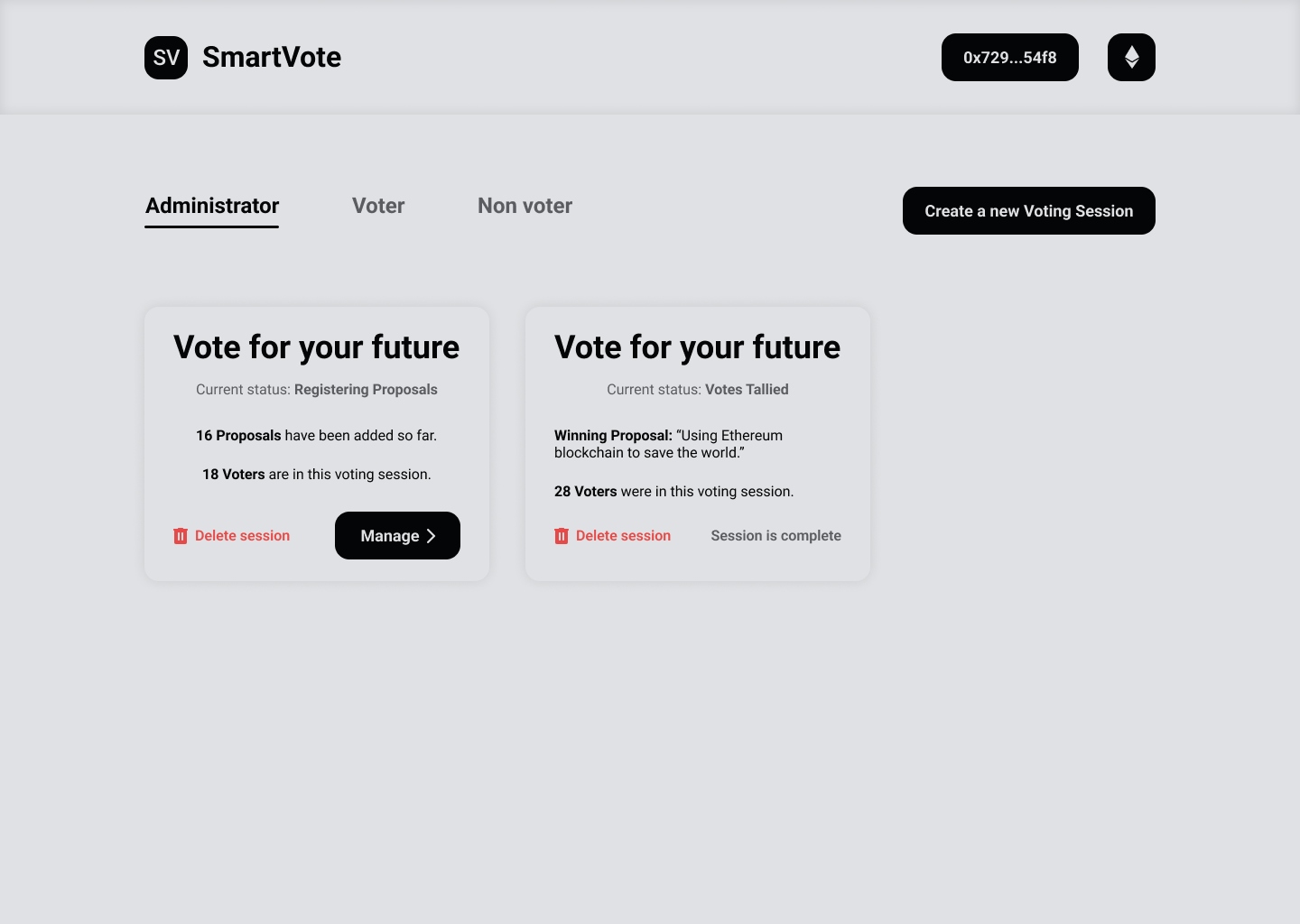
SmartVote allows users to organize their own voting instances, add users to a whitelist, create proposals, and tally votes. It works on the Polygon and Avalanche blockchains. In general, SmartVote is designed to work with any public or private EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) blockchains.
Technologies Used
The front-end development of the project involves Next.js for web development, Rainbow Kit for linking to the user's digital wallet, and Ethers.js for blockchain communication. Wagmi.sh is integrated to streamline blockchain connectivity and serve as a global state manager.
The blockchain development utilizes Hardhat, a platform for smart contract development, with some contracts implementing the EIP-1167 (Minimal Proxy Contract). Additionally, the smart contracts are pausable to enable users of the dApp to propose the "deletion" of a voting instance (since classic deletions are impossible on the Blockchain), and they are upgradeable to allow cloning and registration of a new contract owner.
Security features are provided by OpenZeppelin, Chai is used for unit testing, and Eth-gas-reporter tracks gas costs on the blockchain. Solidity Coverage measures code coverage during unit tests. Finally, to streamline the retrieval of events recorded on the blockchain, The Graph has been added to the project.
Features
Front-end
The user can create and deploy a new voting instance, add users to a whitelist, create proposals, and tally votes. The user can also view the voting instance details, including the number of proposals, the number of votes, and the number of users in the whitelist.
Blockchain
The SmartVote dApp uses three different smart contracts to work properly:
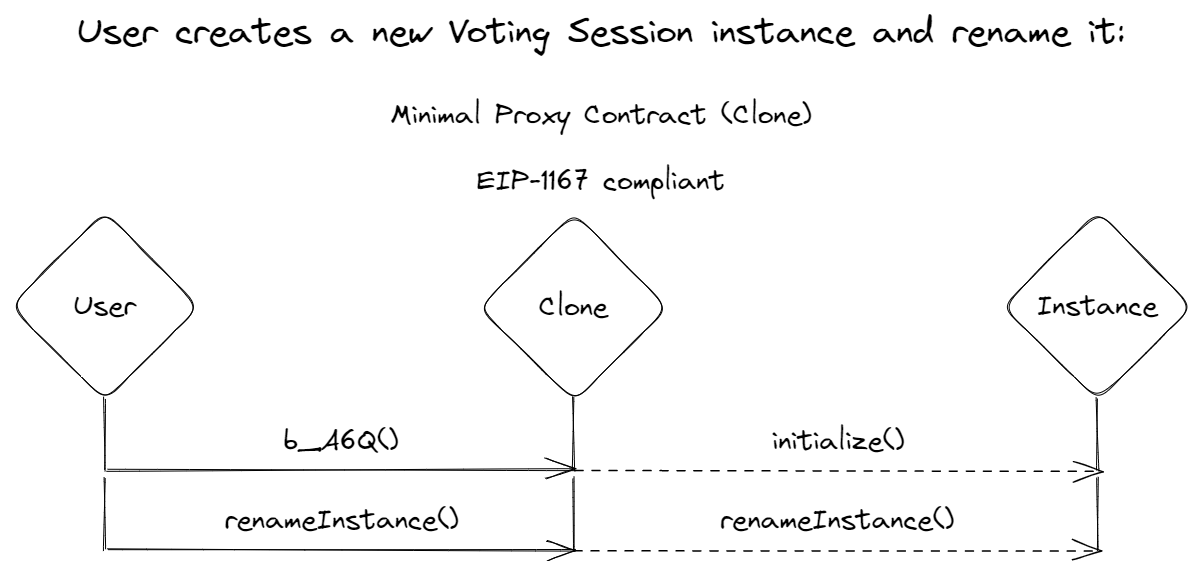
VotingFactory.sol allows the creation of voting instances in accordance with EIP-1167. While it adds an additional cost of 700 gas per iteration, EIP-1167 simplifies the VotingFactory contract and greatly reduces deployment costs;
VotingHandler.sol serves as a reference to the clones created by VotingFactory. This smart contract contains all the logic for voting sessions, including adding voters, adding proposals, counting votes, and managing second rounds. Additionally, VotingHandler is upgradeable to enable cloning and registration of a new contract owner. Moreover, it is pausable to propose to smart contract owner the "deletion" of a voting instance.
InstancesList.sol acts as a bookmark, allowing non-voters to follow or stop following a voting instance from their dashboard.